In the graphic and web design, designer really must consider the colors used in the design to set the right mood and to convey a deliberate feel or emotion that supports the information within design. Let’s take a look at the color wheel for a quick review of color!
The three primary colors are: red, blue and yellow.
And the three secondary colors are orange, green and violet. The secondary color are created by combining two adjacent primary color.
Then, if you combine a primary color with a secondary color, you will get what’s called teriary color. Example: Yellow and green create yellow-green, red and orange create red-orange,…
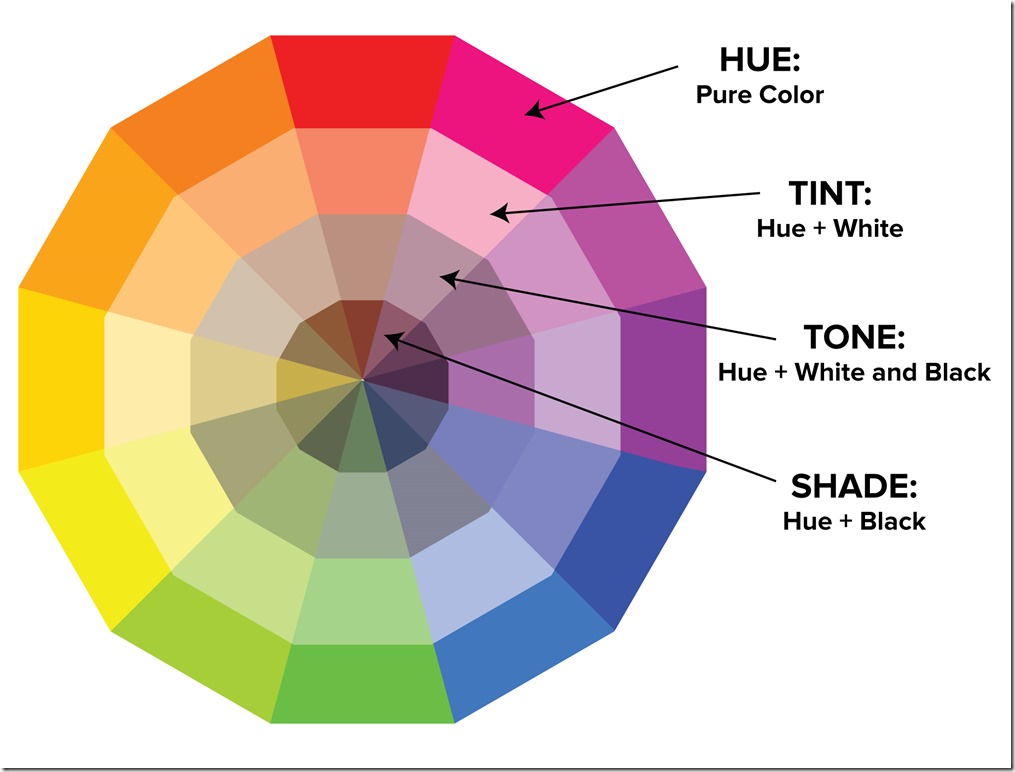
So, What happens when you add white to a color? Well, you get what’s called a tint. The more white you add to a color the lighter the tint. Similarly, when you add black to a color, you get what’s called a shade. The more black you add, the darker the shade. Here’s a look at the complete color wheel with all of the primary, secondary, and teriary color along with each of their tints and shades:
Some Color harmonies:
- Monochorme: Monochrome color represent a single color and all of its interations from white to black, example:
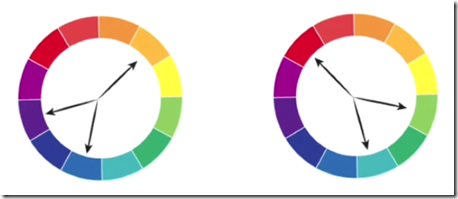
- Complementary: Complementary color represent a pair of color at opposite ends of the color wheel, example: red vs green, violet-red vs green-yellow:
- Split complementary: Split complementary color harmonies are created when you select a main color like yellow-orange, and the choose two colors on either side of that first color’s complement, here is blue and violet, or instance is red vs green-yellow and blue-green.
- Analogous(adjacent): Analogous colors or adjacent colors, are created when you pair any 2 or more colors that are right next to each other on the color wheel, example: orange-yellow vs yellow, or blue, blue-violet, violet:
- Triad: Triads are any three colors that are equally distant on the color wheel, like violet-red, orange-yellow, and blue-green, or red-orange, green-yellow and blue-violet, …







EmoticonEmoticon